TECHNOLOGY
TECHNOLOGY
Optomap
Why is imaging so important?
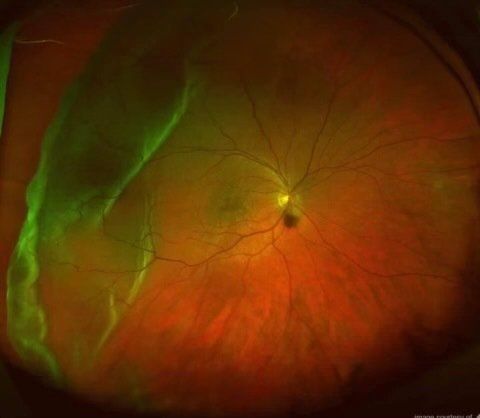
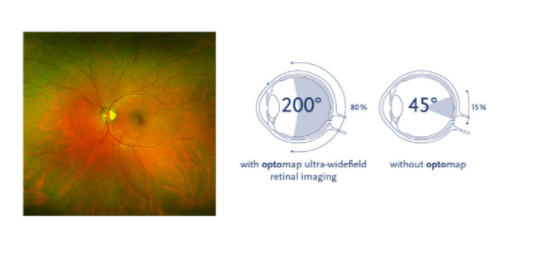
Optomap retinal imaging equipment is one of the most significant breakthroughs in recent visual health assessment. It allows us to see the retina's blood vessels, directly see eye diseases, and make a very accurate diagnosis. In addition, Optomap enables us to find signs of other underlying conditions, such as stroke, heart disease, high blood pressure, and even diabetes, all of which are visible in the retina.
Preventing Diseases with Imaging
When we conduct an eye exam for you, our goal is to look at the structure and function of your eyes. We try to pinpoint the earliest signs of problems or potential complications so that we can effectively prevent, diagnose, and treat conditions such as:
- Macular degeneration
- Glaucoma
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Cataracts
- Retinal detachment
- We can do this with Optomap because it provides more information for your eye doctor to use.
When the retina detaches, it is lifted or pulled from its normal position. If not treated promptly, a retinal detachment can cause permanent vision loss. Anyone can get a retinal detachment; however, those who are nearsighted, those over the age of 50, those who have had significant eye injuries, and those with a family history of retinal detachments are more likely to experience it.

OCT
Optical Coherence Tomography
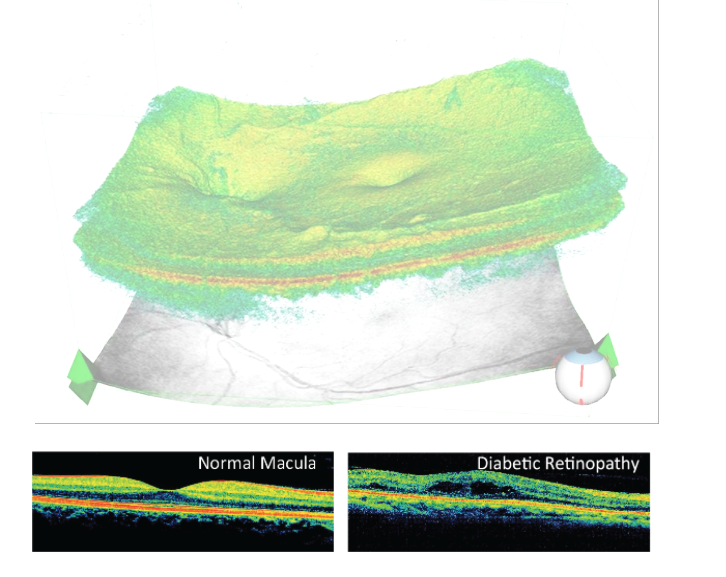
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCTs) is an imaging technique that uses light waves to capture visual information within the patient's body, similar to an optical ultrasound. It allows you to capture the retina and anterior segment images, which help diagnose and treat diseases such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic macular edema.
When used to evaluate the retina, it provides high-resolution scans of retinal anatomical parts allowing the ability to detect and monitor various conditions such as macular degeneration and macular edema due to diabetic retinopathy.
OCT can also be used to evaluate the integrity and quality of the optic nerve. It can detect small changes in the retinal nerve fiber attributed to damage due to glaucoma. Vision loss due to glaucoma cannot be restored; therefore, early detection is critical. If not treated, glaucoma can lead to blindness.
Visual Field
Visual Field Testing
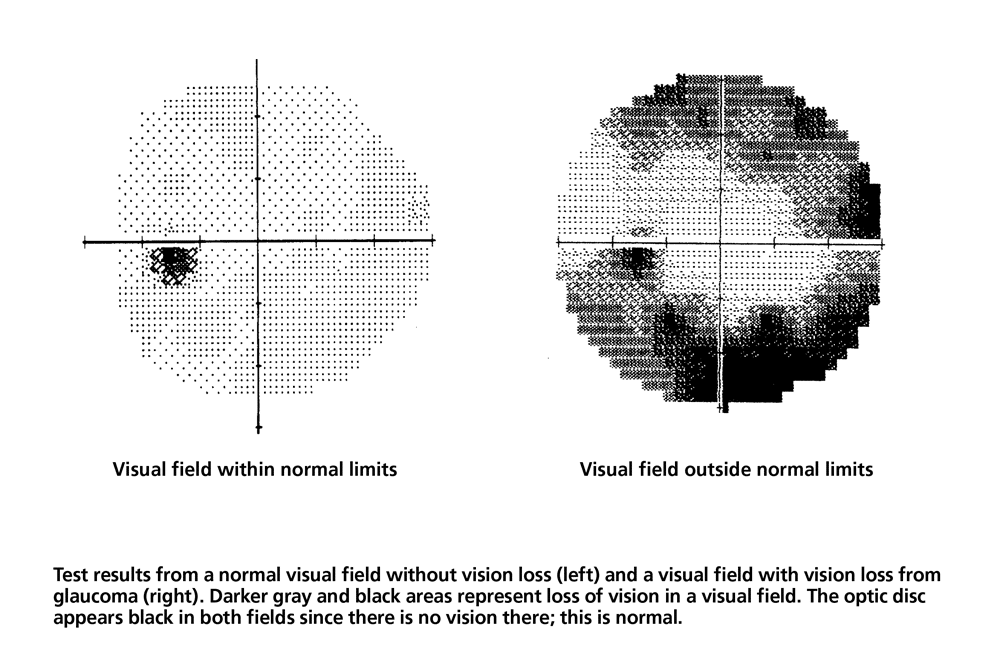
Visual field testing measures how far each eye sees in every direction without having to move your head or your eyes. It can also detect how sensitive your eyes are in some regions of the visual field. This test allows the doctor to see or rule out certain ocular diseases or injuries, such as glaucoma.
What is a Visual Field Test?
With a normal and healthy eye, we can see a wide range of space in front of us without having to turn our heads or move our eyes, which includes the area that would be considered your peripheral vision. The visual field is the whole range of space that we can see collectively.
Our vision is typically the best right in the center of our visual field, which is why when you are trying to look at objects, you move them in front of you or turn your eyes towards them. The visual field tests measure two things:
How far left, right, up, and down the eye sees without moving your head or eye.
How sensitive the vision is in different areas of our visual field.
Why do people need a visual field test?
The doctor might recommend a visual field test to check for early signs of diseases, such as glaucoma that can damage the eyes if not treated. Some people diagnosed with ocular conditions like glaucoma may not notice any noticeable changes to their vision. Still, this test will allow the doctor to see any changes or vision loss in their peripheral vision.
VEP
Visual Evoked Potential Testing
Visual evoked potential (VEP) is a highly-advanced vision test that objectively measures how well your entire vision system works. The results of this VEP vision test will help your doctor diagnose various vision disorders and better understand when changes in your visual function occur.
What is a visual evoked potential (VEP) vision test?
When light from an image enters your eye, it is turned into electrical energy by cells in the retina – the light-sensitive layer at the back of your eye. These cells send the electrical energy back to the visual cortex, the part of your brain where the image is processed.
VEP, or Visual Evoked Potential, uses visual stimuli from a computer screen in different patterns and contrasts to elicit the electrical response from your retina. The electrical energy is then sent to your visual cortex, where the Diopsys® VEP vision test records the electrical signal and creates a report for your doctor. It is similar to an EKG but for your entire vision system.

ERG
Pattern Electroretinography (ERG) Vision Testing
Pattern electroretinography (pattern ERG) is a highly-advanced vision test that objectively measures how well your visual system works. Information from this test will help your doctor diagnose various vision disorders and better understand when changes in your visual function occur.
What is a pattern ERG vision test?
When light from an image enters your eye, it is turned into electrical energy by cells in the retina. Pattern ERG, or electroretinography, uses visual stimuli from a computer screen in different patterns and contrasts to elicit that electrical response. The electrical energy created is measured by the Diopsys® PERG vision test and used to generate a report for your doctor. It is similar to an EKG but for your eyes.
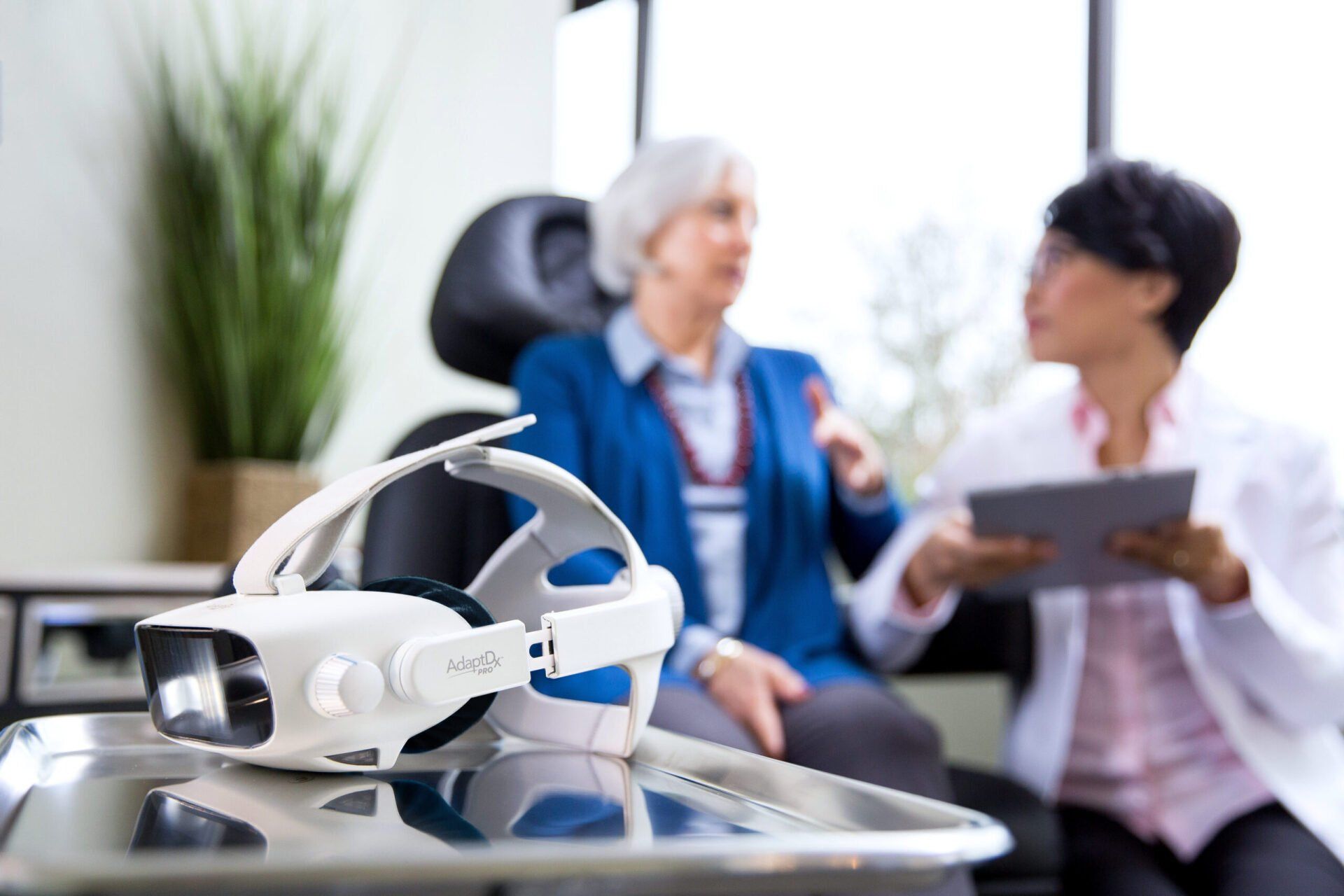
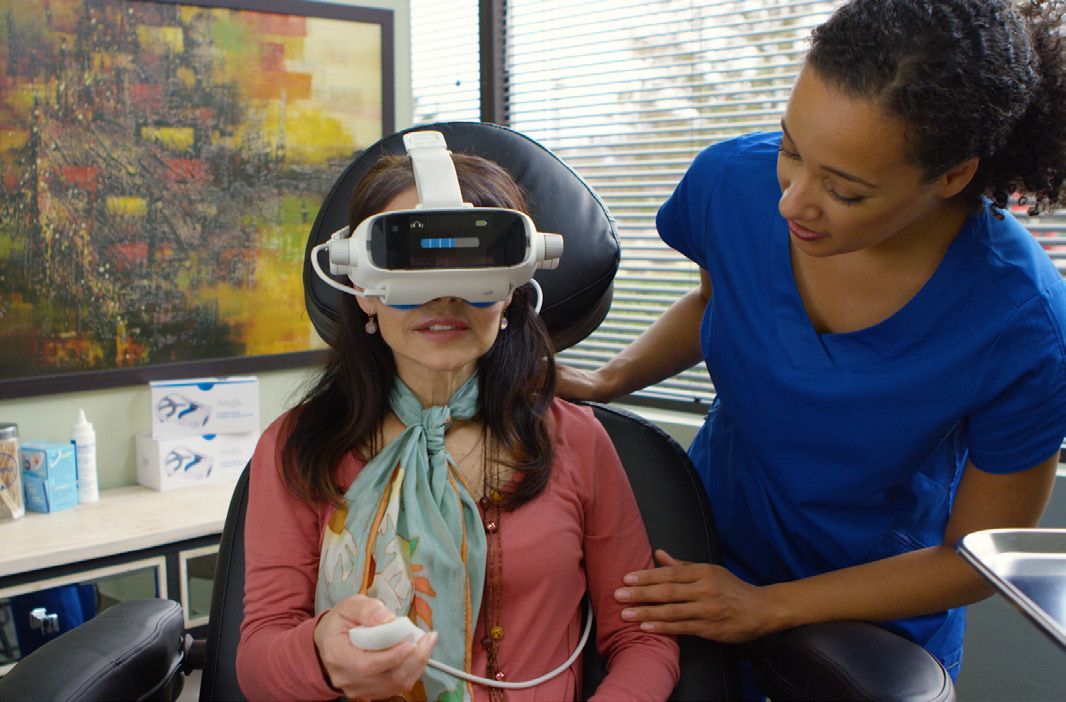
AdaptDX
AdaptDx Dark Adaptometer
The AdaptDx Dark Adaptometer is a diagnostic device that helps eye care professionals diagnose and monitor age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a progressive condition that affects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, and is the leading cause of vision loss in people over the age of 50. The device measures the time it takes for the eye to adjust to low light levels, a process known as dark adaptation. This measurement, known as the dark adaptation curve, is used to diagnose AMD at an early stage and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The AdaptDx Dark Adaptometer is a non-invasive, easy-to-use device that can be used in a standard eye exam setting and requires no patient dilation.
AMD can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages because it often does not cause any symptoms. By the time symptoms appear, the condition has often progressed to a more advanced stage and vision loss may be permanent. Early detection and treatment of AMD are important for preserving vision and preventing vision loss. The AdaptDx Dark Adaptometer helps eye care professionals detect AMD at an early stage, allowing them to provide more personalized treatment to their patients and potentially preserve their vision.


Topography
Topography
The topography of the eye refers to the three-dimensional surface contour of the cornea, the clear outer covering of the eye. It plays an important role in the focusing of light onto the retina, which is responsible for transmitting visual information to the brain. By accurately mapping the topography of the eye, eye care professionals can diagnose and treat various visual impairments, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and keratoconus. A corneal topography examination can also help in the detection of conditions such as corneal dystrophies, corneal scars, and corneal infections. Additionally, the topography of the eye is also useful for monitoring the progression of these conditions and for evaluating the outcomes of surgical procedures, such as LASIK, that alter the shape of the cornea.